What is K417n Mutation?
My Geek Score: As viruses interact with the environmental pressures of selection, they can transform and develop, generating variants that may possess increased virulence. Some of the primary concerns that public health officials have as these new variants continue to emerge include their viral transmissibility, reinjection rate, disease severity, and vaccine efficacy.
If we consider DNA information as a series of sentences, mutations are errors in the spelling of words. Composes these sentences. Sometimes mutations, like a misspelled word, become insignificant, the meaning of which is still unclear.
How do RNA viruses transform?
It possesses single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid (ssDNA) and many times more than those with double DNA -braided (dsDNA). Not all mutations increase virulence, and, in most cases, they may, in fact, necessarily be detrimental or inconsistent.
Therefore, organisms must balance a high mutation rate that allows them to adapt to changing environmental conditions and a low one that lessens the incidence of catastrophic mutations. Small DNA viruses can encode their DNA repair, and some RNA viruses also share the ability to check for and repair replication traps.
However, while DNA viruses generally rely on the host cell’s transcription machinery, RNA viruses encode their own transcription machinery. This means that the rate of RNA virus replication and mutation is more directly related to its genome and is thus subject to the same evolutionary pressures.
The offspring of RNA viruses, with genomes, commonly falling in the 7-12 kilobase (kb) length range. It tends to support one or two distinct mutations per site of the nucleotide. The Asian pneumonia coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) genome is probably around 27-31 km long, increasing the total number of detected mutations without necessarily increasing the incidence rate.
The ability to rapidly detect new genetic characteristics allows viruses to emerge on new hosts, avoid vaccine-induced immunity, and become more virulent. On the other hand, this ability can also be a double-edged sword in improving overall genome fitness. The World Health Organization (WHO) recently announced a nomenclature system for SARS-CoV-2 of naming and searching that will help public debates of variants as they emerge. This nomenclature system was developed by virological, microbial, terminology, and communication specialists worldwide to ensure that SARS-CoV-2 variants are easy to pronounce and avoid any potentially deleting terms. To this end, the expert group convened by the WHO has recommended using letters of the Greek alphabet as names for each new SARS-CoV-2 variant.
B.1.351 also the N501Y mutation. Strain B.1.351 is also known as 20C / 501Y.V2 or the beta variant. The SARS-CoV-2 beta variant was first discovered in South Africa in October 2020 and has been found in more than 48 other countries since then.
Strain B.1.351 has the following dominant mutations:
- N501Y
- K417NE484K
This South African variant is believed to be about 50% more transmissible than the earlier variants identified in South Africa. To date, the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine is 75% effective against infection with this variant. Furthermore, the vaccine efficacy against severe, critical, or fatal disease due to SARS-CoV-2 illness with this variant, as well as variant B.1.1.7, is 97.4%.
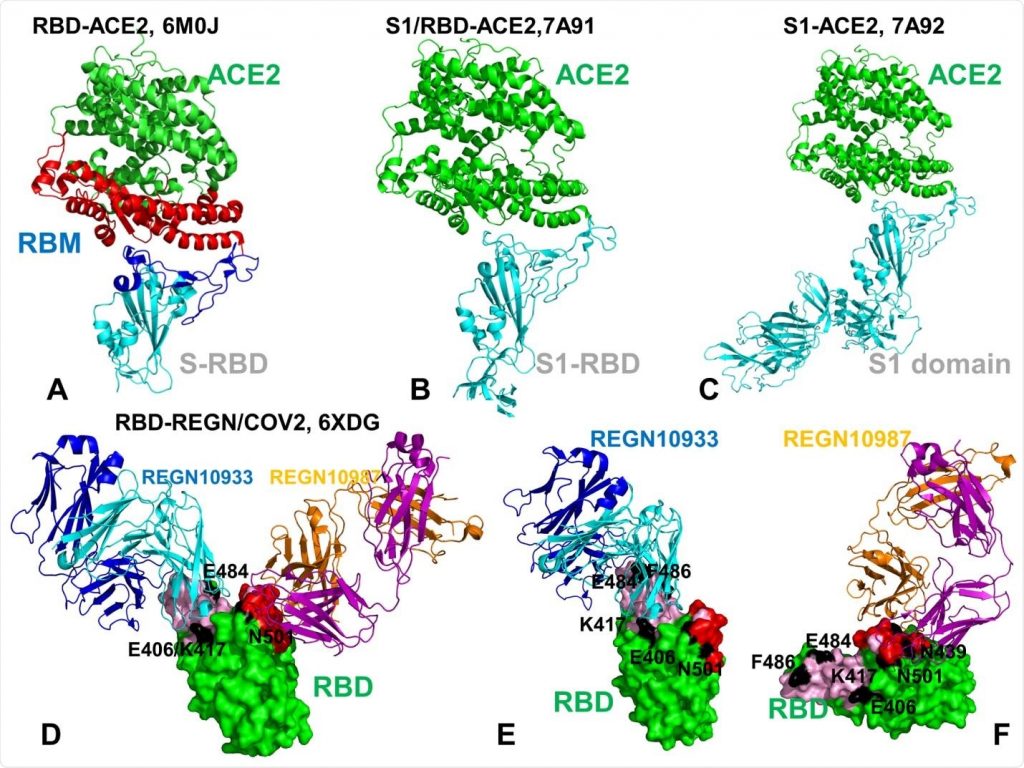
K417
This peak protein mutation has been found in several lineages, including P.1 and B.1.351. It makes the bind cells of the virus tighter.
Which regions of the SARS-CoV-2 genome transform the most?
A large meta-study carried out by Koyama, Platt, and Parida (2020) collected over 10,000 SARS-CoV-2 genomes worldwide and compared them to discover the most common mutations, identifying almost 6,000 distinct variants.
The most divergent segment of the genome was ORF1ab, which is the largest, occupying about a third of the genome. Some of these proteins are the target of the remdesivir antivirus drugs and favipiravir, which can cause concern regarding the development of a strain against which these drugs have no effect. The second diverse region of the SARS-CoV-2 genome is around the spike protein, which must remain largely conserved to interact with ACE2. Some mutations, such as D364Y, have been reported to increase the structural stability of the spike protein, increasing its affinity for the receptor. However, most are likely to lessen the virulence of the virus to such an extent that the lineage quickly dies away. Know the Symptoms Covid 19 Delta Variation in Kids